Notion has exploded in popularity as an all-in-one workspace, used by individuals, startups, and global companies alike. At first glance, it seems like a note-taking app, but beneath the surface lies a powerful database engine that can transform how teams manage projects. The real magic happens when you use relational databases and dashboards—tools that allow you to connect information, automate insights, and centralize operations.
This article will walk you step by step from a blank Notion page to building a fully functional project management dashboard with advanced relational databases.
Why Use Notion for Project Management?
While Asana, Trello, and ClickUp provide predefined structures for tasks, Notion takes a different path. It’s a blank canvas where you design your own system.
Benefits of using Notion for projects include:
- Customization: Build workflows that mirror how your team actually works.
- All-in-One Hub: Combine project tasks, documentation, wikis, and meeting notes in one place.
- Scalability: Works for freelancers, small teams, and larger organizations.
- Relational Power: Connect tasks, projects, and resources for deeper insights.
The flexibility is both a blessing and a challenge—it requires thoughtful setup but rewards you with unmatched control.
Step 1: Create Core Databases
Every advanced Notion setup begins with databases. Think of them as digital spreadsheets with superpowers.
Suggested Core Databases
- Projects Database
- Properties: Project Name, Owner, Status, Deadline, Priority.
- Tasks Database
- Properties: Task Name, Assignee, Due Date, Status, Related Project.
- Resources Database
- Properties: Document Name, File Link, Resource Type, Related Project.
- Meetings Database (optional but powerful)
- Properties: Date, Attendees, Notes, Linked Project.
By starting with these four, you can manage tasks, resources, and documentation under one roof.
Step 2: Establish Relations Between Databases
The next step is to connect your databases using relations. Relations let one database “talk” to another.
Examples of Relations
- Link tasks to projects so you see all tasks within a specific project.
- Link resources (briefs, contracts, reports) to projects for easy access.
- Link meeting notes to both projects and tasks.
This allows information to flow seamlessly across your system.
Step 3: Use Rollups to Generate Insights
Once databases are related, you can use rollups to extract data.
Practical Rollup Examples
- Show the percentage of completed tasks inside each project card.
- Display the nearest upcoming due date from linked tasks.
- Summarize how many resources are attached to a project.
Rollups act like formulas, turning raw data into meaningful insights automatically.
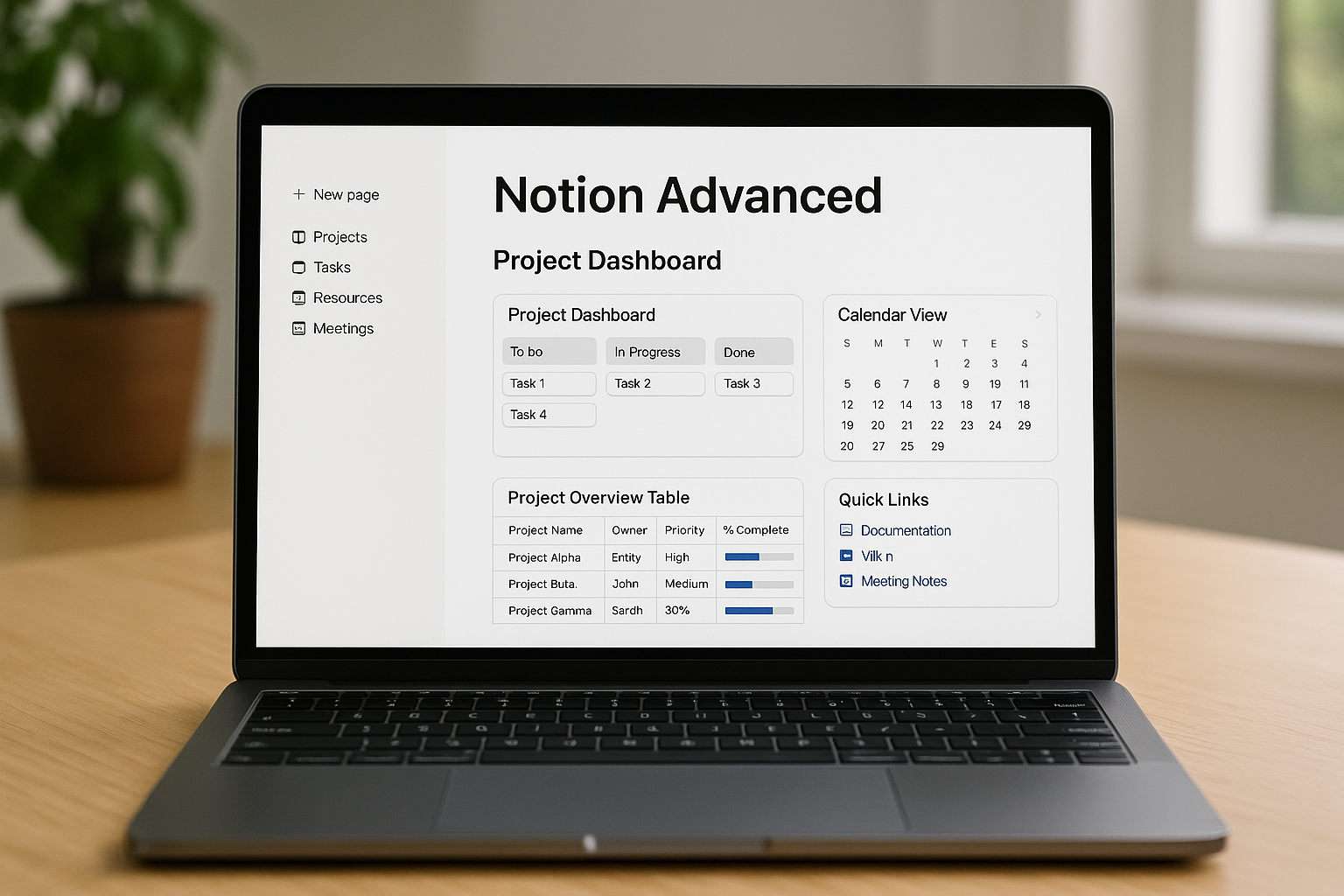
Step 4: Build the Project Dashboard
Dashboards are Notion pages where you combine linked views of databases.
Components of a Dashboard
- Kanban View of Tasks: Display tasks grouped by status (To Do, In Progress, Done).
- Calendar View: Visualize deadlines across all projects.
- Project Overview Table: List projects with owners, priorities, and completion percentages.
- Quick Links Section: Buttons or links to important documents, wikis, or meeting notes.
- Metrics Section: Use rollups and formulas to track progress at a glance.
This dashboard becomes your team’s command center, replacing multiple apps and spreadsheets.
Step 5: Add Templates for Consistency
To scale your system, use Notion’s database templates.
- Project Template: Includes default properties like kickoff date, milestones, and a linked task view.
- Task Template: Preloaded with checklists, tags, and assignee fields.
- Resource Template: Ready for uploading briefs, contracts, or deliverables.
Templates reduce setup time and ensure every project follows the same structure.
Real-World Use Cases
Marketing Agency
- Projects Database: Each client campaign is a project.
- Tasks Database: Writers, designers, and account managers linked to projects.
- Resources Database: Store creative briefs and deliverables.
- Dashboard: Shows campaign deadlines, client status, and content pipelines.
Startup Product Team
- Projects Database: Each feature or release cycle is a project.
- Tasks Database: Engineering tickets linked to sprints.
- Resources Database: Store specs, wireframes, and API docs.
- Dashboard: Combines roadmap, release schedule, and progress charts.
Freelancers
- Projects Database: One project per client.
- Tasks Database: Track deliverables and deadlines.
- Resources Database: Store contracts, invoices, and feedback.
- Dashboard: Gives a big-picture view of ongoing and completed work.
Advanced Tips for Power Users
- Use formulas to calculate urgency, such as “Days until deadline.”
- Create personal dashboards filtered by each team member’s tasks.
- Integrate with tools like Slack, Google Calendar, or Zapier for notifications.
- Leverage Notion widgets (progress bars, countdowns) for visual cues.
- Combine Notion AI for quick summaries, drafting, or meeting note cleanups.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overbuilding Early: Keep the system simple until the team adapts.
- Ignoring Relations: Without links, databases become isolated silos.
- Not Using Templates: Leads to inconsistent project structures.
- Skipping Reviews: Dashboards should be updated regularly to remain useful.
Comparing Notion with Competitors
- Vs. Asana: Asana is better for structured task management; Notion excels at flexibility.
- Vs. Trello: Trello is faster to learn; Notion is more customizable for integrated knowledge and tasks.
- Vs. ClickUp: ClickUp has more built-in project features; Notion offers better documentation and relational power.
For teams that value control and all-in-one integration, Notion often wins.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Notion
Strengths
- Maximum customization for diverse workflows.
- Combines tasks, notes, and databases seamlessly.
- Affordable compared to enterprise-level tools.
Weaknesses
- Steeper learning curve for beginners.
- Can be slow with very large databases.
- Requires time investment for proper setup.
Final Thoughts
Notion is more than just a workspace—it’s a platform where teams design their own productivity ecosystem. By mastering relational databases, rollups, and dashboards, small and medium teams can build a custom project management system that rivals specialized software.
If you’re willing to invest time in setup, Notion rewards you with a powerful, flexible, and unified tool. From freelancers to startups and agencies, it adapts to the way you work rather than forcing you to adapt to it.